Simplifying Lyophilization With Decades of Experience
Lyophilized beads (lyo-beads) or Lyophilized beaded reagents (LBRs) are changing the game in diagnostics by providing stable, cost-effective reagents that are easy to rehydrate — a major step up from traditional lyophilized powders. But to get the most out of these benefits, you need the right expertise.
With over three decades of experience and a collaborative approach, we aim to simplify your lyophilization needs for molecular and point-of-care diagnostics. No need to stress over expensive or time-consuming process changes.
Count on us for expert support, scalable production, and ISO certified quality that meets your unique needs.
Achieve High Quality and Compliance
Extension of your team to develop custom lyophilization formulations that prioritize risk mitigation:
- Robust quality management system ensures traceability and proactive risk assessment.
- ISO 13485 certified, 21 CFR 820 compliant, and aligned with cGMP standards.
- Three decades of quality expertise to streamline processes for successful outcomes.
Accelerate Time-to-Market
Move seamlessly from concept to market with our proactive, efficient approach:
- Rapid identification and resolution of complex challenges.
- Access to proprietary excipients that streamline development.
- Proven processes for smooth technology transfers without quality compromises.
- Integrated optimization and scale-up services to ensure on-time delivery.
Adapt and Scale with Ease
Scale confidently with high-quality LBRs from 3µL to 75µL, ensuring reliable performance and streamlined supply chain management for diverse applications:
- Ensure production capacity of up to 20 million beads per month with flexible dispensing options to meet both small and large-scale needs.
- Offer comprehensive pack-out capabilities, including direct bead integration, custom assembly, and final packaging with quality control testing.
- Handle complex reagents such as magnetic beads, colorimetric and fluorescent conjugates, PCR components, antibodies, and proteins.
- Support ultra-sensitive diagnostics, point-of-care solutions, quantitative lateral flow, CRISPR diagnostics, and isothermal amplification.
The Science of Uniform Lyophilized Beads for Versatile Applications
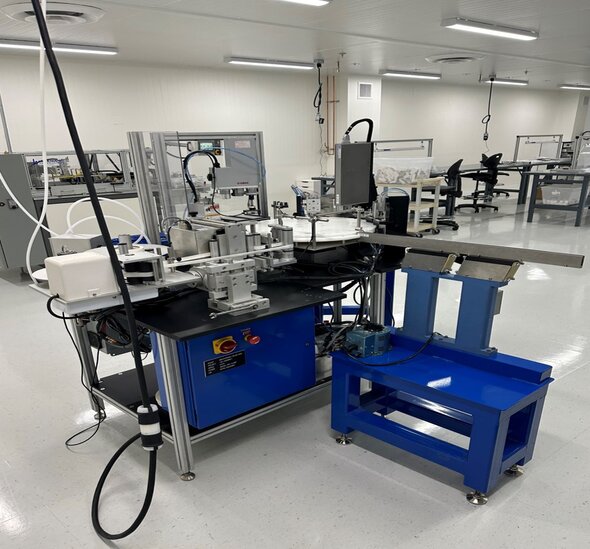

Pick & Place Bead Dispensing
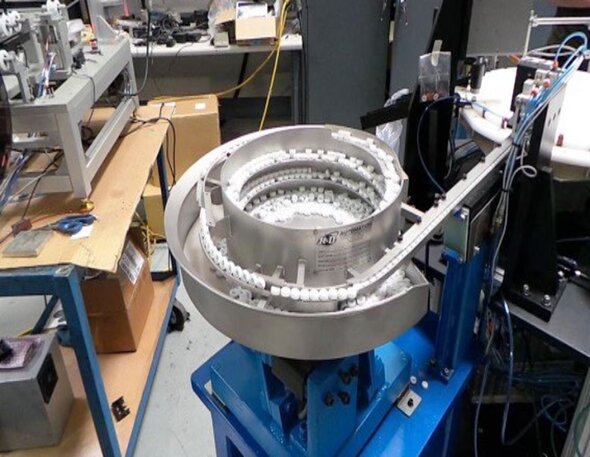

Vial Filling & Capping

Dry Room Operation
Our innovative lyophilization process produces structurally sound, active beads. Using controlled sublimation and proprietary excipient technology, we ensure consistently spherical beads that maintain integrity and activity.
Our extensive experience spans diagnostic areas such as respiratory diseases, cardiovascular conditions, sepsis detection, and STI diagnostics, allowing us to implement effective, tailored solutions rapidly.
Why Partner With Fortis Life Sciences for Lyophilized Beads?
Proven Expertise
With 25+ years of experience and a deep understanding of lyophilization, our team anticipates challenges and consistently delivers successful outcomes for our clients.
Flexibility and Customization
Where challenges arise, our innovation excels. We strive for genuine collaboration to develop tailored formulations and processes, adapting to your evolving needs.
End-to-End Solutions
From formulation development to final product manufacturing and QC testing, we provide comprehensive services to simplify your supply chain.
Driving Diagnostic Excellence
We invest in the latest technology and proactively enhance our processes to deliver reliable solutions in diagnostic development.
FAQs
Q. What is lyophilization?
A. Lyophilization is a dehydration process where water or a solvent is removed from a material by sublimation to create a stable preparation. The material is first frozen to solidify the liquid and then subjected to reduced pressure. As the temperature is increased, the frozen water or solvent undergoes sublimation, transitioning to vapor without first passing through the liquid phase. This removes the frozen molecules from the material. A drying phase removes any remaining water or solvent.
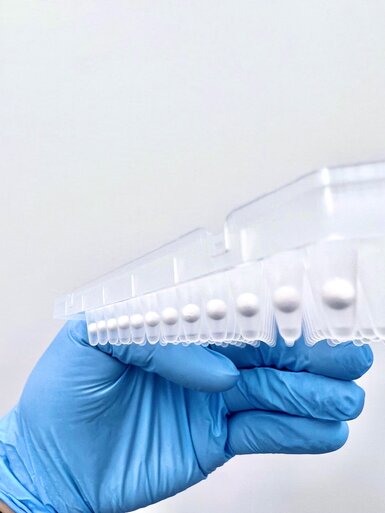
Q. What are lyophilized beads?
A. Lyophilized beads start as a formulation that typically consists of a buffer, excipient(s) to provide structure and mechanical strength, and the critical reagent, antibody, conjugate, magnetic particle, etc., at a defined concentration. The formulation is dispensed into liquid nitrogen in precise, uniform droplets, frozen, collected, and then lyophilized. This process ensures that the chemical or biological activity of the reagent is preserved.
These lyo-beads can then be used in medical devices and molecular and point-of-care diagnostics to preserve, maintain the integrity of, and deliver critical reagents. Addition of a solvent such as water restores the reagent/molecule to its original state.
Q. What are the benefits of lyophilization in point-of-care diagnostics?
A. Packaging and delivering critical reagents and other molecules in lyophilized beads offer many advantages for medical devices and point-of-care diagnostics:
- Enhanced stability of sensitive chemicals and biologicals and a longer shelf life
- Simplified storage, transportation, and handling
- Rapid rehydration and reconstitution while maintaining structural integrity and functionality of the critical reagent/molecule
- Improved solubility compared to non-lyophilized materials
- Eliminates the need for aliquoting and freezing following reconstitution
- Reduced risk of contamination due to the elimination of liquid from the formulation and eliminates or reduces the need for anti-microbial agents
- Enables increased flexibility in package design for the assay or medical device
- Increased cost effectiveness due to ambient temperature storage and shipping methods
Q. What are lyophilized control swabs?
A. Lyophilized swabs are typically used for quality control of lateral flow assays that detect the presence of infectious pathogens such as those causing COVID-19, seasonal flu, and tuberculosis. Protein, DNA, RNA, or inactivated control strains can be lyophilized onto a swab to mimic processing of a patient sample and are intended for use in healthcare settings to test the functionality of every component of the assay.