Ran Proteins in Health and Disease
Ras-related nuclear protein (Ran), a member of the Ras superfamily of small GTPases, plays a critical role in the transport of macromolecules between the nucleus and the cytoplasm that occurs through nuclear pores. More recently, research has shown that Ran participates in the coordination of mitosis, with specific roles in mitotic spindle assembly, centrosome duplication, microtubule dynamics, and chromosome alignment.1
Ran acts as a molecular switch, cycling between GTP-bound and GDP-bound conformations. RanGTP is generated in the nucleus by the guanine nucleotide exchange factor RCC1, while GTP is hydrolyzed to produce RanGDP in the cytoplasm by GTP-hydrolysis activating protein 1 (RanGAP1) with the help of Ran-binding protein 1 (RanBP1).2 Additional effectors of Ran include other Ran-binding proteins, such as RanBP3 that enhances the rate of nuclear export3, and importins alpha and beta, critical mediators of nuclear import.2
Ran and its binding proteins are implicated in a variety of diseases. For example, elevated levels of Ran and RanBP1 are found in many cancers, including ovarian, colon, esophageal, lung, and lymphoma2. RanBP2 is also implicated in cancer, as mice lacking the gene are prone to spontaneous tumors4. In addition, a mutation in RanBP2 causes a familial form of acute necrotizing encephalopathy, a rare and often-fatal neurological disorder that affects otherwise healthy children after a viral infection such as influenza5. Both RanBP3 and RanBP5 are involved in influenza virus replication6. RanBP9 is elevated in the brains of patients with Alzheimer disease, where it is thought to promote generation of the toxic neuropeptide amyloid beta and enhance mitochondrial-mediated apoptosis7,8.
Ran and its wide range of effector proteins play a significant role in many functions in the cell, providing insights into a number of different processes, especially in cell division and the life cycle. However, because of the wide breadth of activities, these proteins also critical players in multiple disease processes, rendering the knowledge gained from these proteins critical for both cell biology and human health.
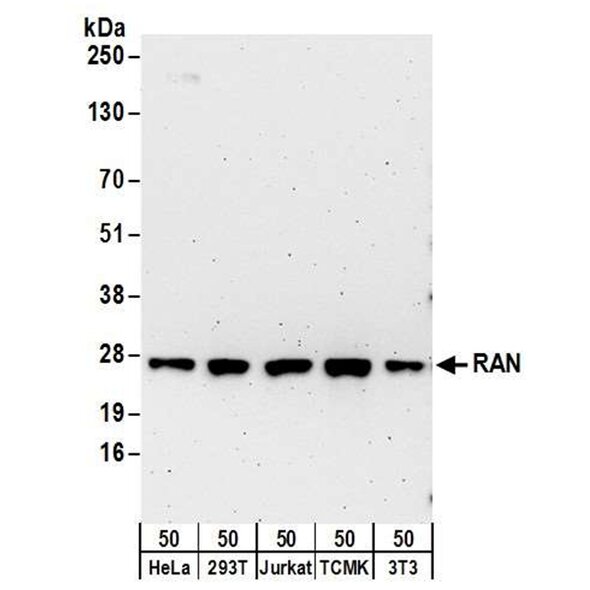
Bethyl offers the following antibodies for use in Ran Protein research
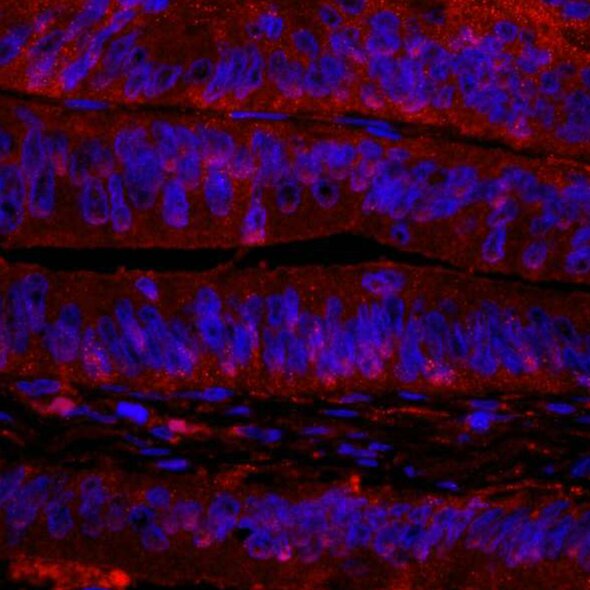
Detection of human RanBP1 in FFPE colon carcinoma. Antibody: Rabbit anto-RanBP1 (IHC-00441). Secondary: DyLight® 594-conjugated goat anti-rabbit IgG (A120-201D4). Counterstain: DAPI (blue).
References
- Clarke PR, Zhang C. 2008. Spatial and temporal coordination of mitosis by Ran GTPase. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. Jun;9(6):464-477.
- Rensen WM, Mangiacasale R, Ciciarello M, Lavia P. 2008. The GTPase Ran: regulation of cell life and potential roles in cell transformation. Front Biosci. May 1;13:4097-40121.
- Lindsay ME, Holaska JM, Welch K, Paschal BM, Macara IG. 2001. Ran-binding protein 3 is a cofactor for Crm1-mediated nuclear protein export. J Cell Biol, Jun 25;153(7):1391-1402.
- Dawlaty MM, Malureanu L, Jeganathan KB, Kao E, Sustmann C, Tahk S, Shuai K, Grosschedl R, van Deursen JM. 2008. Resolution of sister centromeres requires RanBP2-mediated SUMOylation of topoisomerase IIalpha. Cell. Apr 4;133(1):103-15.
- Neilson DE, Adams MD, Orr CM, Schelling DK, Eiben RM, Kerr DS, Anderson J, Bassuk AG, Bye AM, Childs AM, et al. 2009. Infection-triggered familial or recurrent cases of acute necrotizing encephalopathy caused by mutations in a component of the nuclear pore, RANBP2. Am J Hum Genet. Jan;84(1):44-51.
- Predicala R, Zhou Y. 2013. The role of Ran-binding protein 3 during influenza A virus replication. J Gen Virol. May;94(Pt 5):977-984.
- Woo JA, Jung AR, Lakshmana MK, Bedrossian A, Lim Y, Bu JH, Park SA, Koo EH, Mook-Jung I, Kang DE. 2012. Pivotal role of the RanBP9-cofilin pathway in Aβ-induced apoptosis and neurodegeneration. Cell Death Differ. Sep;19(9):1413-1423.
- Liu T, Roh SE, Woo JA, Ryu H, Kang DE. 2013. Cooperative role of RanBP9 and P73 in mitochondria-mediated apoptosis. Cell Death Dis. Jan 23;4: e476.