Uracil-DNA Glycosylases (UDGs)
Carryover Prevention for qPCR and RT-qPCR
Uracil-DNA Glycosylase (UDG) catalyses the release of free uracil from uracil-containing DNA. UDG efficiently hydrolyzes uracil from single-stranded or double-stranded DNA. This helps preserve the integrity of DNA samples and improves the accuracy and reliability of your PCR and RT-qPCR reactions. At Fortis we have three UDGs options available and they can be customized to fit your needs!
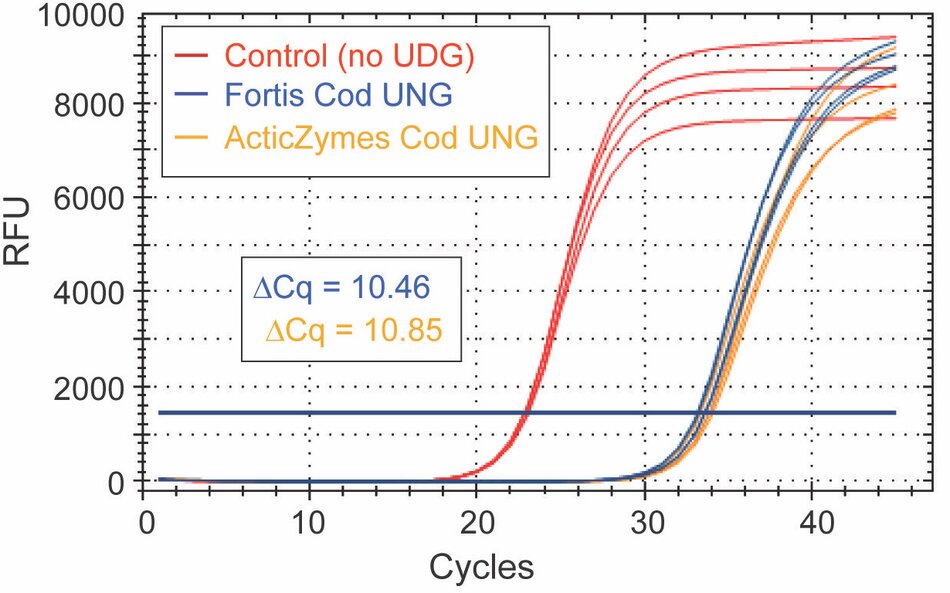
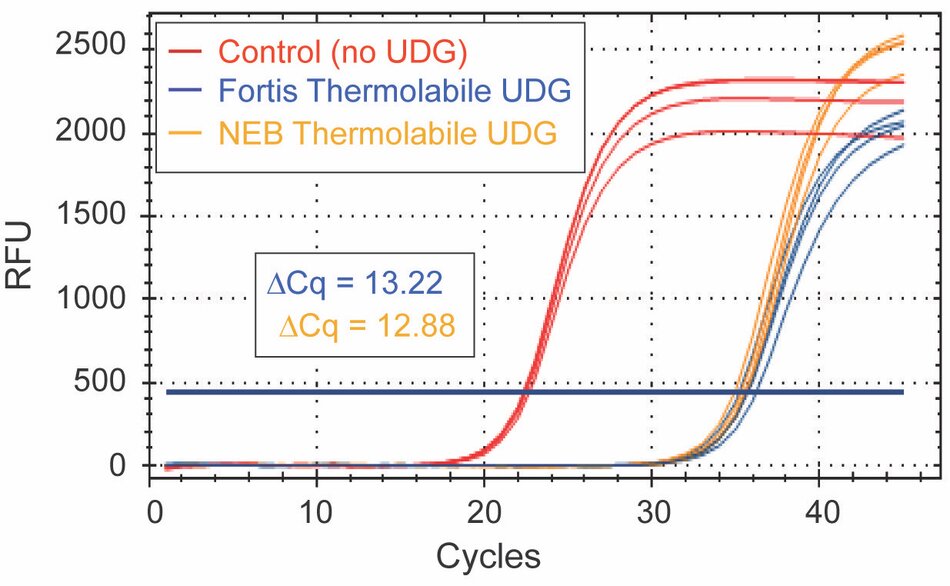
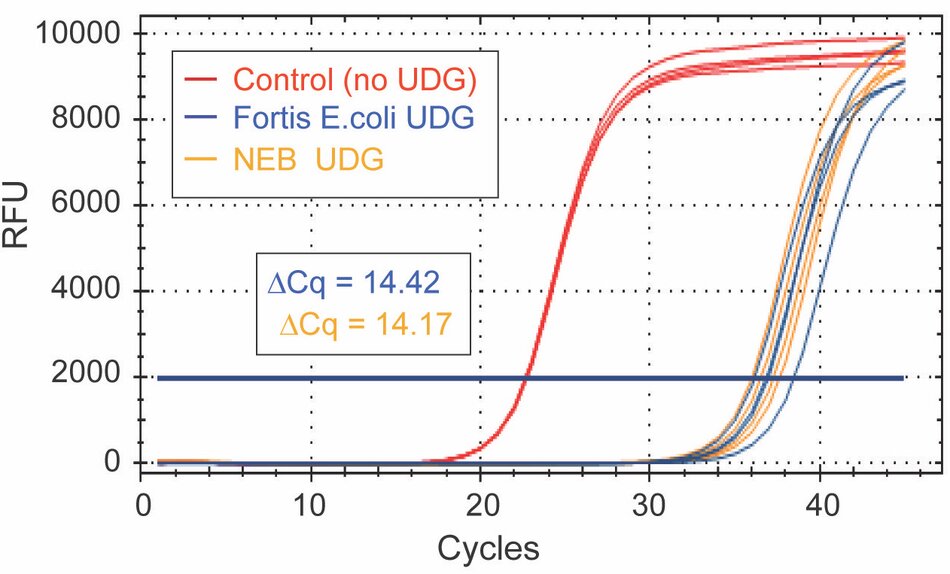
The following experiments compare UDGs in a qPCR assay using primers and probe specific to a uracil-containing template. The uracil-containing template is a representation of carry-over contamination. A No-UDG Control (red) is included to demonstrate product digestion. ΔCq measures product digestion by calculating the difference with and without treatment of each UDG. The greater the ΔCq, the more efficient product digestion.

Contact us for a Custom Quote
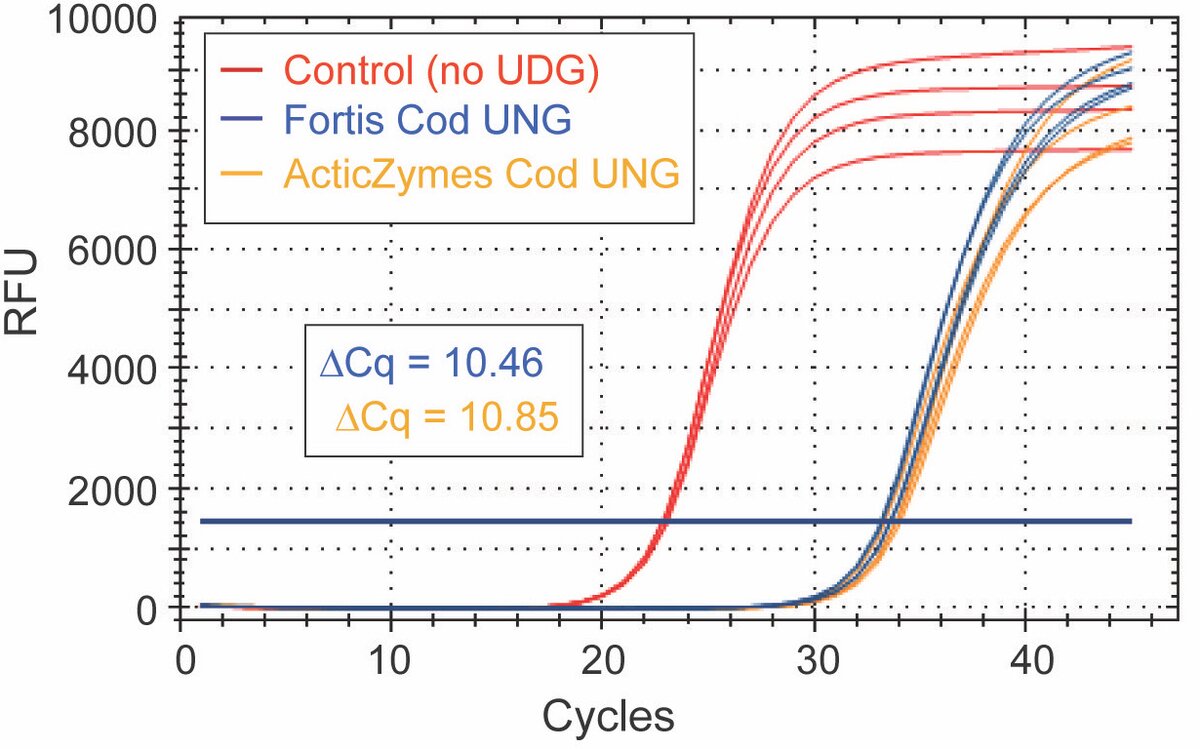
Fortis Cod UNG (blue) vs. ArcticZymes (orange). Control (red) demonstrates product digestion after a 5 minute incubation at 25 °C.