Focus on Nanomaterials
Gold, silica, iron oxide, and poly-lactic-co-glycolic acid (PLGA) nanoparticles are revolutionizing nanomedicine in a variety of fields, from oncology and immunology, to neurology, infectious disease, and more. Researchers and commercial organizations alike are harnessing the unique properties of these nanoparticles to transform therapeutic treatments, drug delivery, and theranostics.
Gold nanoshells absorb and scatter light, enabling targeted cell destruction in photothermal therapy while providing exceptional stability and biocompatibility. The tunable optical properties of gold nanorods make them ideal for applications in imaging and photothermal therapy. Iron oxide nanoparticles, with their magnetic properties, facilitate targeted delivery, enhance drug accumulation at specific sites, and invoke hyperthermia. Through their spacious internal structures, mesoporous silica nanoparticles provide efficient drug encapsulation and controlled release. PLGA nanoparticles can also encapsulate a wide range of drugs for controlled systemic and local delivery in a highly biodegradable platform.
These versatile nanoparticles are propelling nanomedicine forward, with potential for improved therapeutic outcomes and enhanced patient care.
Resources
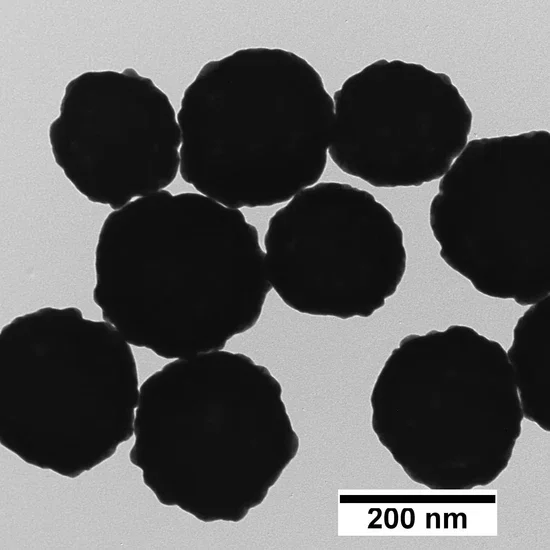
What are Gold Nanoshells: What are their properties?
Gold nanoshells are surface plasmon resonant (SPR) nanoparticles consisting of a nanoscale silica core surrounded by an ultra-thin gold shell. Changing the ratio of the core diameter and the shell thickness tunes the absorption and scattering properties of the nanoshells across the visible and near-IR (NIR) regions of the electromagnetic spectrum. Increasing the size of the silica core, and decreasing the thickness of the gold shell cause the plasmon resonance to shift toward the NIR.
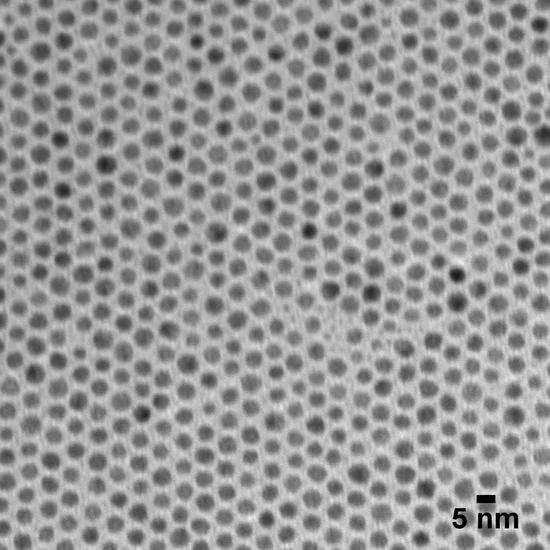
Gold Colloid Formulation & Application Information
Gold colloid – sometimes referred to as "colloidal gold" – is a suspension consisting of sub-micron gold nanoparticles suspended within a solvent, most often water. Gold nanoparticles have unique optical, electronic, and thermal properties and are being incorporated in a wide variety of technologies including microscopy, electronics, diagnostics, and therapeutics.
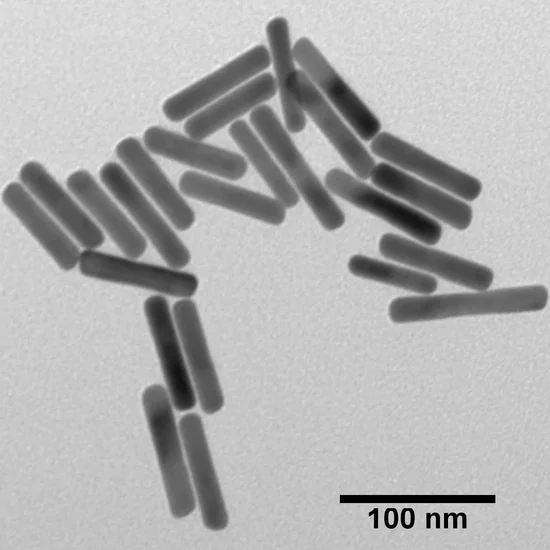
Introduction to Gold Nanorods
Our gold nanorods are surface plasmon resonant (SPR) rod-shaped nanoparticles with narrow size distributions and uniform shape. The gold nanorods have absorption peaks that are tunable throughout the visible and short wave near-infrared (SWNIR) regions of the electromagnetic spectrum. Our purification methods remove ammonium surfactants used during synthesis and replace it with citrate, producing a stable, easily displaceable surface chemistry to use as a base for functionalization with a wide variety of molecules (silica, DNA, antibodies, etc.). We also offer PEG-functionalized nanorods, as well as carboxyl-terminated surfaces for bioconjugation.
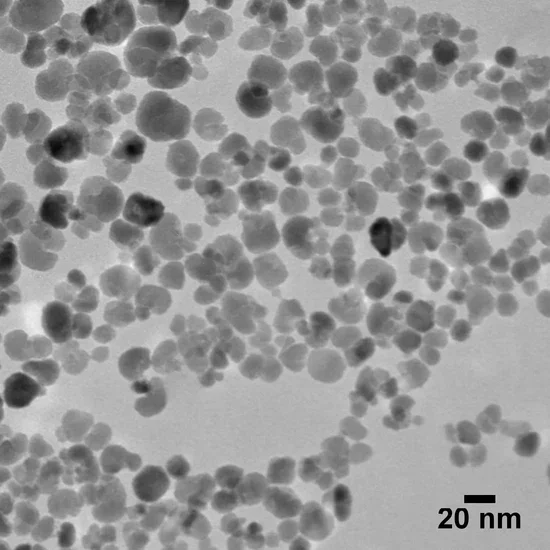
Magnetite (Iron Oxide) Nanoparticles
We have extensive experience with the synthesis and development of complex nanomaterials and coatings, and have produced a broad assortment of well-characterized, precisely-tuned magnetic nanoparticles on a custom basis. We are able to synthesize magnetic nanomaterials of varying compositions, sizes, morphologies, and surface functionalities, examples of which are shown below.
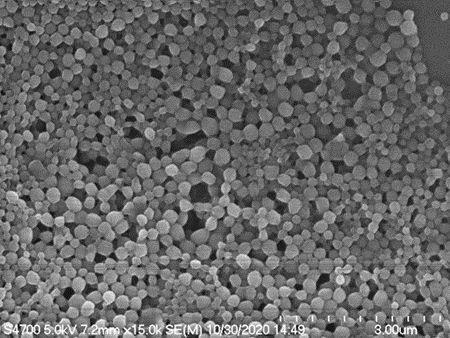
PLGA Encapsulated Nanoparticles
We offer customized encapsulation services and made-to-order PLGA nanoparticle fabrication for applications in drug or gene delivery, theranostics, and tailored to the specific needs of the customer. For common injectable applications, the desirable size range for in vivo delivery vehicles is 100‒300 nm. Our team can encapsulate your desired compound (drug, protein, peptide, nucleic acid) or modify the surface of PLGA particles to facilitate attachment of ligands, antigens, and antibodies in order to meet custom requirements for targeted applications.
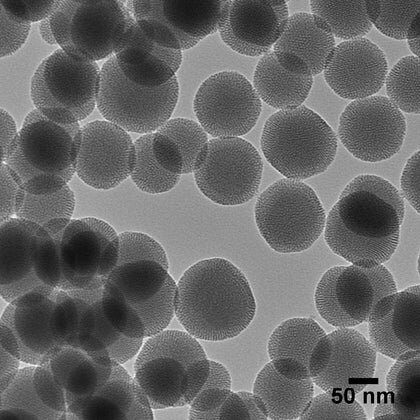
An Introduction to Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles
Mesoporous silica nanoparticles (MSNs) are silica nanoparticles with pores that range in diameter from 2 to 50 nm and have an overall diameter below 1 µm. Their range of pore sizes is consistent with the IUPAC definition of mesoporous and make them ideal materials for applications ranging from catalysis and environmental chemical removal to biomedicine. We bring the synthetic expertise required to tailor the design of MSNs to target an intended application with the utmost control.