Focus on Autophagy
Inside the cell, there are multiple mechanisms to degrade intra- and extra-cellular components. Initially characterized as a starvation response, autophagy is a non-specific pathway that sequesters cytoplasmic contents via double membranes to recycle intracellular contents. When cells are depleted of nutrients, they must break down cellular components that are not necessary to supply the building blocks for those that are. This recycling process – autophagy – is more efficient than creating or manufacturing individual macromolecules. Autophagy is critical for cell and tissue homeostasis and when disrupted, can lead to a variety of disease states including cancer, increased pathogen replication, heart disease, pro-aging, and neurological disorders.
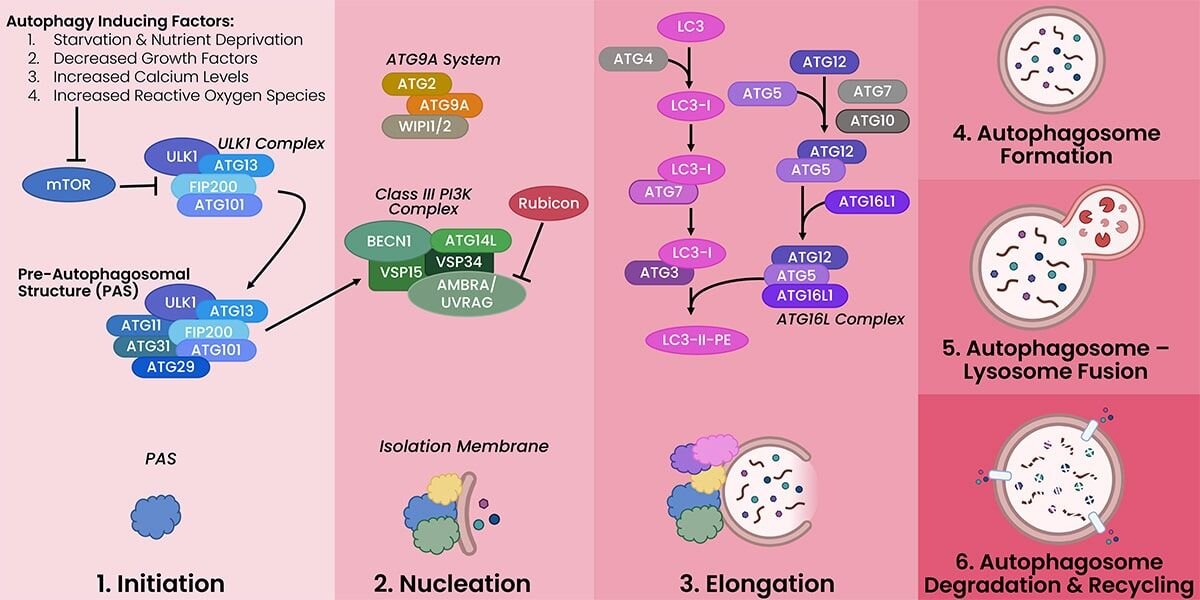
The process of autophagy in six steps:
- Initiation: the clustering of autophagy factors to create the core autophagy complex
- Nucleation: the formation of the initial double membrane at the site of the core autophagy complex
- Elongation: the extension of the double membrane
- Autophagosome Formation: the complete enclosure of cytoplasmic contents by the double membrane forming the autophagosome
- Autophagosome-Lysosome Fusion: the fusion of the lysosome and the autophagosome, exposing the contents of the autophagosome to the degrading enzymes of the lysosome
- Degradation & Recycling: the breakdown of the autophagosome contents by lysosomal enzymes resulting in building blocks that can be released back into the cytoplasm and used to make DNA, RNA, proteins, lipids, and carbohydrates
Cutting-edge Autophagy Research
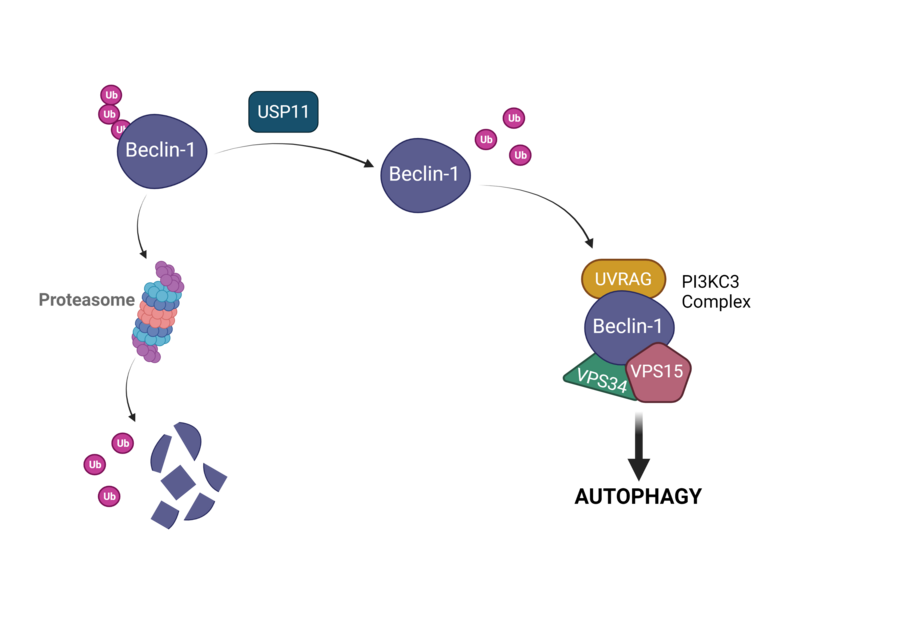
USP11 promotes autophagy
USP11 promotes autophagy by directly stabilizing Beclin-1. A recent publication identifies USP11 as a potential therapeutic target to inhibit autophagy in cancer.
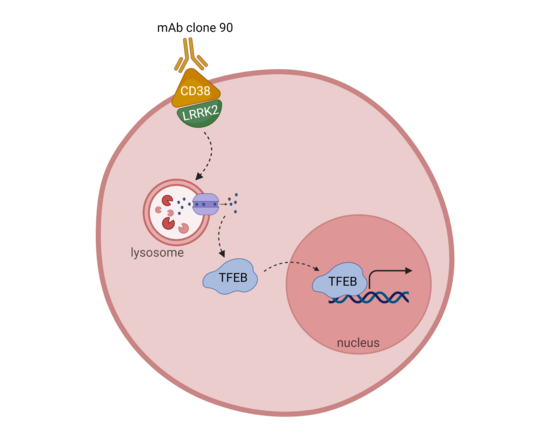
CD38 and LRRK2 play a role in autophagy induction
A recent paper by Neel Nabar and colleagues from the National Institute of Health added new signaling molecules (CD38 and LRRK2) into the autophagy induction pathways.
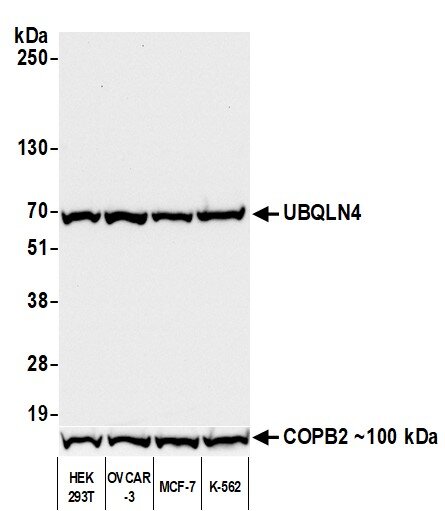
Generation and Application of a Novel Monoclonal Antibody to UBQLN4 to Characterize the dsDNA Damage Response
Ubqln4 plays an important role in autophagy by interacting with the autophagosome membrane and recruiting additional proteins required for autophagosome-lysosome fusion. Learn how Fortis made a highly specific antibody for Ubqln4, using our six pillars of validation approach, that can be used in WB, IP, flow cytometry, and multiplex IHC.
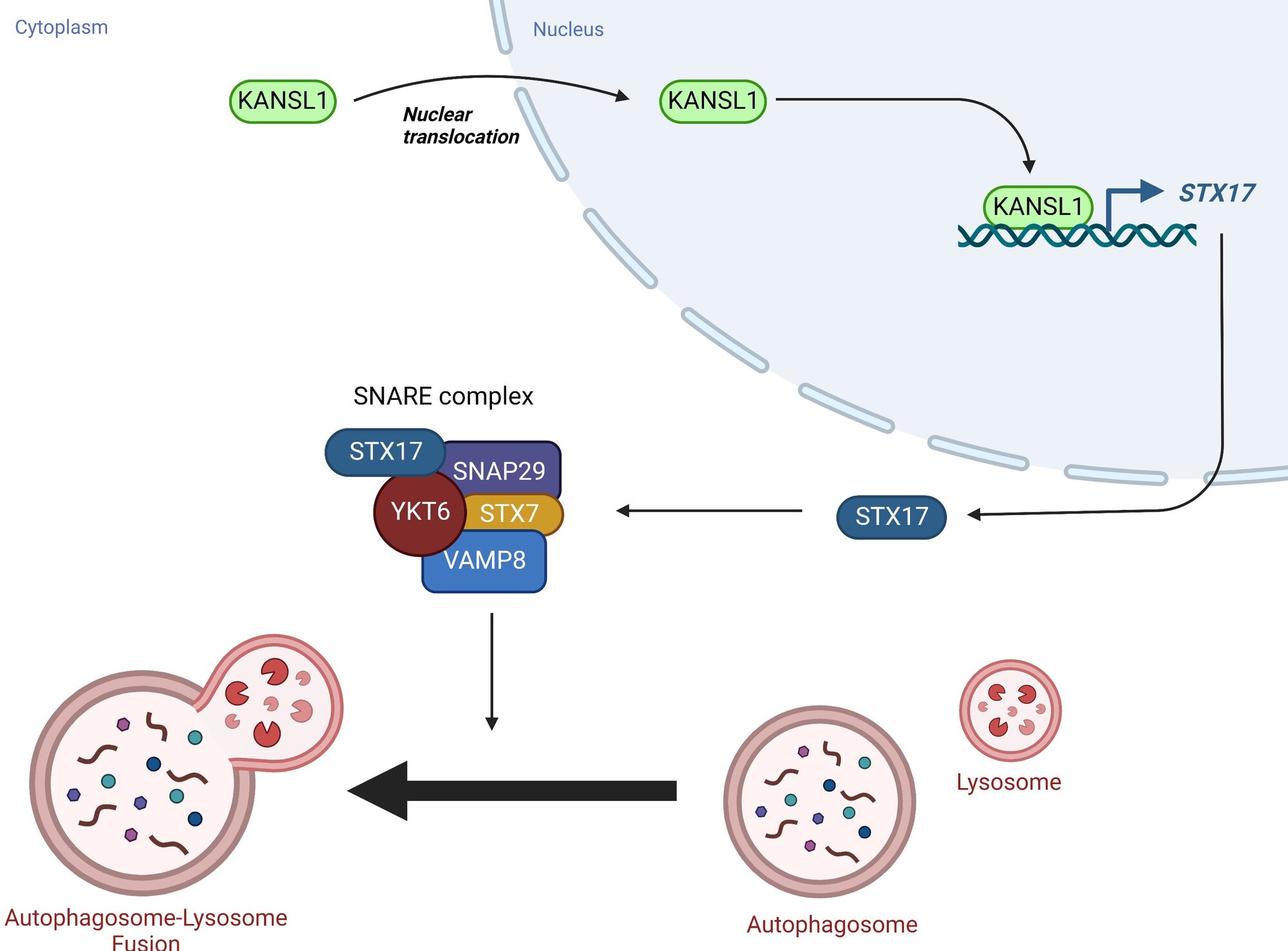
KANSL1 is a regulator of autophagosome-lysosome fusion
A recent study shows a link between autophagy and a rare genetic disorder, Koolen-de Vries syndrome, caused by loss of KANSL1. An FDA-approved drug, 13-cis retinoic acid, was able to rescue autophagy in the absence of KANSL1.
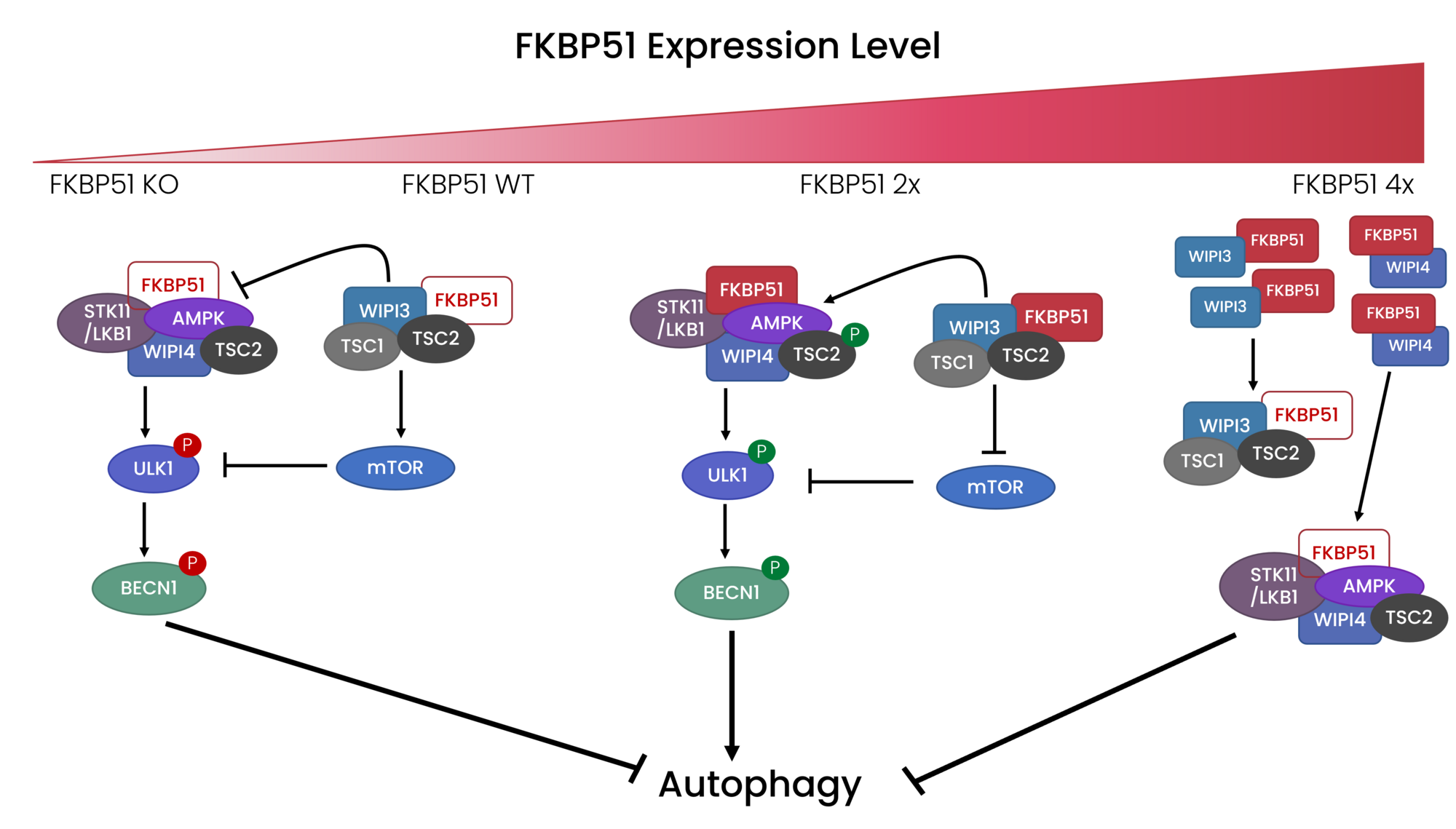
FKBP51 links autophagy and obesity
FKBP51 expression levels tightly control induction or inhibition of autophagy. In the mediobasal hypothalamus, this regulation of autophagy has a profound impact on obesity.
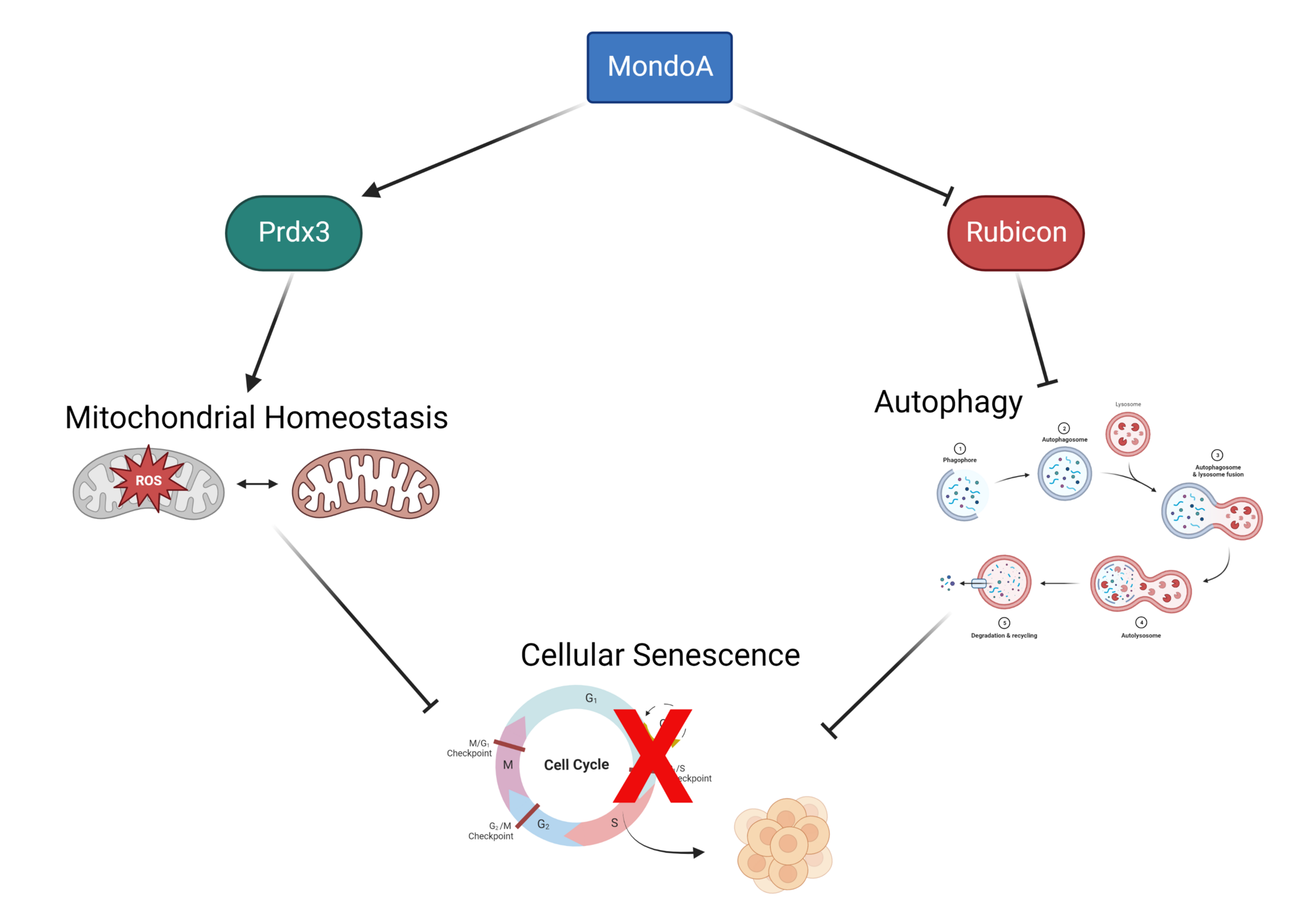
MondoA controls senescence through autophagy and mitochondrial homesostasis
A recent study provides mechanistic insights for the involvement of autophagy in cellular senescence. This research shows the transcription factor MondoA controls expression of the autophagy inhibitor Rubicon when senescence is induced.